![]()
Most solid tumor cancers express high levels of this calcium ion channel and the flood of calcium into the cell triggers cell growth, proliferation and metastases. It promotes a pathway that stops the self-destruct sequence (apoptosis) present in all healthy cells. Inhibiting TRPV6 normalizes intracellular calcium – reducing the activity of genes associated with cancer cell growth, proliferation and metastases and lifts the inhibition of apoptosis. TRPV6 thus represents a compelling target for the development of new cancer treatments.
TRPV6 is one of approximately 26 functional ion channels in the super-family of TRP channels. TRPV6 is selective for calcium ion and is constitutively active.
TRPV6 is now recognized as an oncochannel and its gene is classified as an oncogene or proto-oncogene.

TRPV6 Channel (Side View)

TRPV6 Channel (Top View)
Saotome, K., Singh, A., K. Yelshanskaya, M. V. and Sobolevsky, A. I. 2016. Crystal structure of the epithelial calcium channel TRPV6. Nature. 534 (7608): 506-511.
Overexpression of TRPV6 has been reported in many human cancers. Large amounts of TRPV6 mRNA have been found in a colorectal cancer cell line (SW480) and a chronic myelogenous leukemia cell line (K-562). Up-regulation of TRPV6 mRNA is reported for prostate cancer and in prostate cancer cell lines LNCaP and PC3. High expression of TRPV6 in breast cancer correlated with pathological parameters. Most strikingly, there is a positive correlation of the TRPV6 mRNA signal with the Gleason scoring of prostate tumors. Immunohistochemical studies show greatly elevated amounts of TRPV6 in carcinomas of prostate, breast, colon, ovary and thyroid. High expression of TRPV6 in breast cancer correlated with pathological parameters and poor patient outcomes. Elevated TRPV6 has also been reported in estrogen receptor-negative breast cancers, and correlated with poor prognosis for patients. Multiple types of ovarian cancer show similar elevated levels of both TRPV6 mRNA and protein.
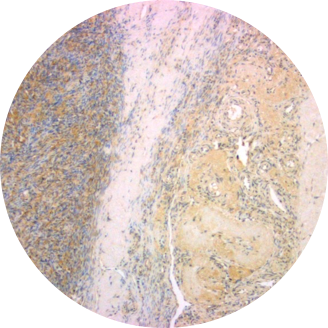
Normal Ovary
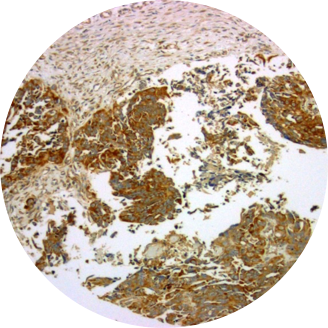
Cancerous Ovary
Overexpression of TRPV6 results in sustained elevation of calcium within the cancer cell. This elevated calcium activates a calcium-dependent calmodulin/calcineurin/NFAT nexus with subsequent activation of genes promoting cell proliferation, metastasis and inhibition of apoptosis (programmed cell death). For more information on role of TRPV6 in solid tumor cancer and its mechanism of action please see our peer reviewed, Journal of Cancer published paper entitled "TRPV6 as A Target for Cancer Therapy".
Soricimed is the first company to develop a specific inhibitor of TRPV6 and to take it into clinical development as a potential treatment for solid-tumor cancers. For more information on our clinical development program please see SOR-C13 - A First-In-Class Drug Candidate in Development for the Treatment of Solid Tumor Cancers. We are also using our knowledge of TRPV6-targeting compounds to deliver highly potent anticancer agents directly to tumors. More information on this program can be found at Peptide-Drug Conjugate Program. Finally, we are developing targeted molecular radiotherapy using our peptides to deliver therapeutic radioisotopes to cancer cells. The approach is known as radioligand therapy (RLT). More information on this program can be found at Radioligand Therapy.
Address
18 Botsford St., Suite 201
Moncton, N.B. E1C 4W7
Canada
T: 506.856.0400
F: 506.856.0414
E: info@soricimed.com
© Copyright 2025 Soricimed Biopharma